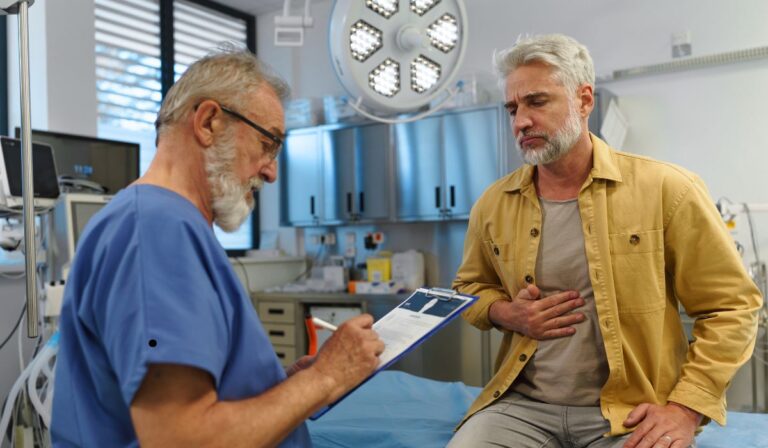
As we age, everyday tasks can become more complicated—eating included. Though it’s often overlooked, difficulty eating is a common challenge among seniors, and it can significantly affect health, independence, and overall quality of life. From chewing discomfort to swallowing challenges, these issues can make mealtimes stressful instead of enjoyable. Understanding why seniors struggle and how to support them ensures they receive the nourishment and dignity they deserve.
Why Eating Becomes Difficult With Age
Several age-related factors can interfere with eating, and sometimes multiple issues occur at once. Here are the most common:
1. Dental Problems and Tooth Loss
When teeth are missing, damaged, or sensitive, chewing can be uncomfortable or painful. Seniors may avoid certain foods—usually the ones packed with nutrients, like crisp vegetables, fruits, and lean meats—leading to nutritional deficiencies. Ill-fitting dentures can also rub, cause sores, or shift during meals. In some cases, solutions such as permanent dentures in Lafayette LA can help restore comfort and confidence at mealtime.
2. Reduced Saliva Production
Dry mouth is a frequent issue among older adults. Aging, medications, or chronic conditions like diabetes can decrease saliva, making chewing and swallowing difficult. Dry mouth can also increase the risk of choking, leading to anxiety during meals.
3. Dysphagia (Difficulty Swallowing)
Dysphagia affects many seniors, particularly those with neurological conditions like Parkinson’s or after a stroke. Food may feel “stuck,” and swallowing can become laborious. Not only does this decrease appetite, but it also raises the risk of aspiration—when food enters the airway instead of the stomach.
4. Decreased Sense of Taste and Smell
As taste buds weaken and senses fade, food may seem bland. Eating becomes more of a chore than a pleasure. Seniors might lose interest in eating simply because nothing tastes good anymore.
5. Medical Conditions and Medications
Chronic illnesses—like dementia, cancer, or COPD—can affect appetite or make eating physically demanding. Certain medications may cause nausea, metallic tastes, or appetite suppression.
Warning Signs to Watch For
Family members and caregivers should be alert to subtle signs that a senior is having trouble eating, such as:
- Taking unusually long to finish meals
- Avoiding certain foods, especially those that require chewing
- Frequent coughing or throat clearing while eating
- Weight loss or clothes fitting more loosely
- Food left untouched on the plate
These signs often point to a deeper issue that needs attention.
The Hidden Risks of Eating Difficulties
If seniors are unable or unwilling to eat properly, their health can decline rapidly. Nutrition fuels every part of the body—immune function, bone strength, muscle mass, even memory.
Eating difficulties can lead to:
- Malnutrition
- Weight loss and muscle weakness
- Dehydration
- Higher risk of falls
- Compromised immune system
Even more importantly, difficulty eating can diminish independence and joy, shifting mealtime from a social experience to a stressful one.
How to Make Eating Easier and More Enjoyable
The good news? There are many ways to support seniors and improve mealtime comfort.
Adjust Food Textures
Soft or easy-to-chew foods can still be delicious and nutrient-rich. Try options like:
- Scrambled eggs
- Oatmeal
- Mashed sweet potatoes
- Puréed or chopped vegetables
- Slow-cooked meats
Simple changes like cutting food into smaller pieces or adding gravies and sauces can also make swallowing easier.
Make Hydration a Focus
Dehydration contributes to chewing and swallowing difficulty. Offer water throughout the day, along with hydrating foods like soups, fruits, and smoothies.
Enhance Flavor and Aroma
To overcome decreased taste and smell:
- Use herbs and spices instead of salt
- Add natural flavor boosters like lemon juice or olive oil
- Serve warm dishes—temperature enhances aroma and taste
Create a Relaxed Mealtime Environment
Seniors eat better when meals are calm and unhurried.
- Turn off the TV
- Use comfortable seating
- Eat together to encourage social connection
Seek Professional Help When Needed
If problems persist, consider consulting:
- A dentist or oral specialist for chewing discomfort
- A speech-language pathologist for swallowing therapy
- A dietitian to build a safe and nutritious meal plan
The Importance of Compassion
Eating difficulties are not just physical—they are emotional. Imagine feeling embarrassed, anxious, or frustrated every time you sit down at the table. Patience and empathy from caregivers and loved ones go a long way in helping seniors feel supported.
In Conclusion
Eating should be enjoyable, not painful or stressful. By recognizing the causes and signs of eating difficulties and making thoughtful adjustments, we can help seniors maintain their health, dignity, and pleasure in food.
After all, mealtime is more than nourishment—it’s connection, comfort, and joy.